Operational Values
There are two different types of Operational Values:
- Resources: All actual or potential assets (except cash) controlled by the organization, that can be exploited in the business processes. Resources compose the infrastructure of the Organization for performing its operations.
- Supplies: Incoming value from Sources, providing benefits to the Organization when performing its operations.
(click on the following elements for more details)
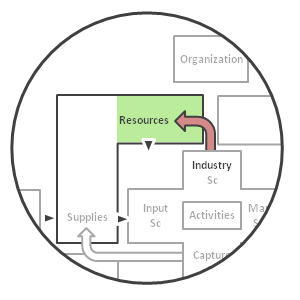
> Resources
(a way to compose the Infrastructure)
CONTEXT
Resources may be:
- unique, rare or widely spread in the industry,
- highly valuable or not in the industry,
- easily imitable or not,
- easily subtitutable or not,
- ...
CONTENT
Resources may be:
- tangible: land, buildings, equipment, machinery, stock of materials,
- intangible: organization, technology, product portfolio, information, intellectual property, design, location, competences, skills, knowledge, methods, rights, relationship, access to supplies, brand, reputation, culture, innovation, management, alliances, equity assets, complementors...
- human.
CONCEPT
Resources may:
- be strategic assets or not,
- be owned, rented or none,
- be located at the organization site, source's site or target's site,
- be exploited by the organization, by sources or targets,
- be strongly or weakly controlled,
- be bought or built,
- be mostly exploited in the Market, Capture or Industry Super-Process,
- be difficult or easy to build,
- be difficult or easy to maintain,
- be difficult or easy to exploit,
- be difficult or easy to control,
- require associated supplies to be exploited (ex: electricity for machines),
- require a low or high level of maintenance,
- improve, stay stable or deteriorate when exploited,
- deteriorate when not exploited (perishable) or not,
- be stable or unstable,
- be in an exploitation phase, a building phase and/or a maintenance phase,
- exist for current exploitation or for potential exploitation (ex: back-up machinery),
- represent a core rigidity (preventing flexibility - ex: exclusive sourcing contract) or not,
- ...
Link with Super-Processes
Resources are the outcome of the Industry Super-Process
(see Process Quadrant)
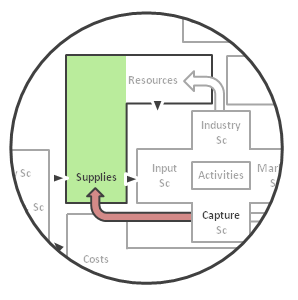
> Supplies
(a way to get the required Benefits)
CONTEXT
Supplies may be:
- new or not for the organization,
- unique, rare or widely spread in the industry,
- similar or differentiated regarding other sources,
- in an introduction, growth, maturity or decline phase,
- part of a highly competitive market between sources or not,
- part of a demand-driven or offer-driven market,
- subject to a make-or-buy decision,
- ...
CONTENT
Supplies may be:
- Operational supplies (incoming goods and services)
- Investments supplies (long-term assets)
- Financial supplies (Securities acquired by the organization, or rights associated with debt or equity securities it issued1)
- Labor supplies (new employees, and work performed by human resources),
- be tangible or intangible,
- be raw materials, intermediate goods, finished goods or services,
- have tangible and/or intangible attributes,
- ...
CONCEPT
Supplies may:
- provide benefits for the organization in terms of costs, technology, time-to-market, availability, image, features, standards, compatibility, customization, associated services, quality, reliability, innovativeness, customer relation, expertise, risk transfer, responsiveness, assurance,
- be stand-alone or associated with other products from third parties,
- be difficult or easy to procure, with regard to competition,
- be difficult or easy to procure, with regard to availability,
- be charged by the source (supplier) or not (contributor),
- be standard or customizable,
- be durable or nondurable,
- need to be replaced or not,
- be mostly used in the Market, Capture or Industry Super-Process, or all,
- be used for the exploitation of a resource (ex: electricity for machines) or not,
- be consumed, modified, incorporated or left unchanged through a process,
- require little or large value added through a process,
- involve low or high potential switching cost for the organization,
- be supplied by one or several sources,
- be beneficial for the business or not (ex: old TV sets that stores are required to take back);
- ...
Link with Super-Processes
Supplies are one of the two outcomes of the Capture Super-Process
(see Process Quadrant)
1- Debt and equity securities can be seen as a stock of rights for future cashflows. When the organization pays the security issuer (coupons, principal or dividends), it actual buys back part of these rights.
Target Values < PREVIOUS - NEXT > Financial Values